Perspectives
Gene therapy: A promising future at a high price
Gene therapy harnesses the body’s own innate capacity to heal itself and changes the face of health care.
May 2, 2023What is gene therapy?
Gene therapy involves the modification or manipulation of a person’s disease-causing gene for therapeutic use (to treat or cure disease). Gene therapy corrects the underlying genetic problem. Gene therapies can be delivered ex vivo or in vivo and can work several ways:
-
- Replacing a disease-causing gene with a healthy copy of the gene
- Inactivating a disease-causing gene that is not functioning properly
- Introducing a new or modified gene into the body to help treat a disease
Gene transfer therapy introduces new genetic material into cells. The therapeutic genes are most often delivered via a carrier, like a vector. The vector is genetically engineered to deliver the gene. Viruses are often used as vectors because they can deliver the healthy genetic material by infecting the cell. (The viruses are modified so they do not cause disease.)1
The vector is injected or given intravenously directly to a specific tissue in the body, where it is absorbed by individual cells.1
Definitions:
Ex vivo is latin for “out of the living.” This means that cells are removed from the patient’s body, modified with new genetic instructions, and then returned to the body to begin altering the faulty disease-causing gene.2
In vivo is latin for “within the living”. In vivo therapy uses viruses or other methods to deliver genes directly into the patient’s cells.2
The idea for gene therapy was first published in 1972, but practical applications weren’t approved in the United States until 2017.
What are the applications for gene therapy?
Gene therapy can be applied in a number of areas, including:
- Oncology
- Musculoskeletal
- Central nervous system
- Endocrine, metabolic and genetic disorders
- Cardiovascular
- Hematology
- Ophthalmology
- Immunology and inflammation
- Infectious diseases
- Dermatology
- Gastroenterology
- Respiratory
- Geriatrics
- Lymphatic, and more
Gene therapies do not always completely cure a disease, but in many cases may improve patient outcomes. Although gene therapy demonstrates a promising future, we are still learning a lot about it and its durability (how long its effects will last in the body).

Gene therapy has a strong outlook
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) anticipates that each year they will receive more than 200 investigational new drug (IND) applications for new gene and cell therapies. By 2025, the FDA expects to approve 10 to 20 new gene and cell therapies per year.3
Gene therapy costs are high
Gene therapy comes with a high cost, due to its complexity to produce and the relatively small population of patients who will be treated.4 The FDA has approved five gene therapies to date.
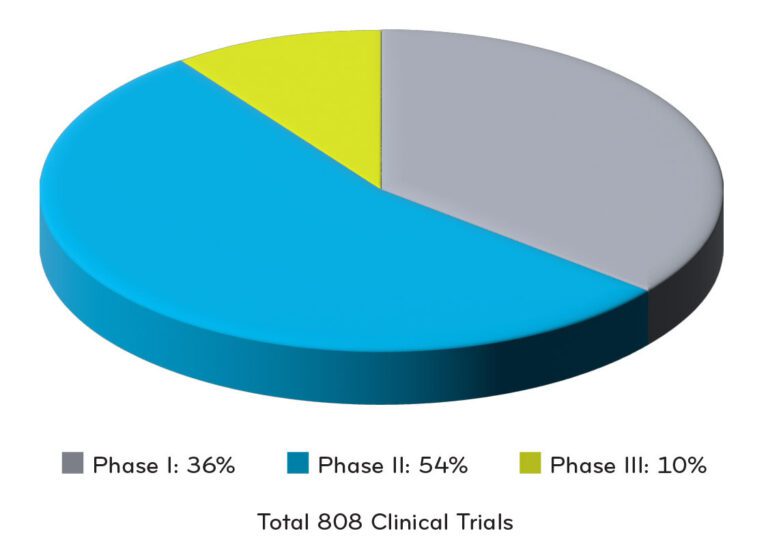 +Clinical data numbers for chart were referenced from Alliance for Regenerative Medicine5
+Clinical data numbers for chart were referenced from Alliance for Regenerative Medicine5
Total of 808 Clinical Trials Underway in North America in 2H 2022:
- 36% in Phase 1
- 54% in Phase 2
- 10% in Phase 3
Approved gene therapy treatments on the market today
Luxturna®: In December 2017, the FDA approved Spark Therapeutics’ Luxturna (voretigene neparvovec-rzyl)5 for the treatment of confirmed biallelic RPE65 mutation-associated retinal dystrophy. It is administered as two separate subretinal injections, one per eye. The wholesale acquisition cost (WAC) of Luxturna is $850,000 per person or $425,000 per eye, not including medical costs.6
Zolgensma®: AveXis’ Zolgensma® (onasemnogene abeparvovec-xioi), is FDA approved for the treatment of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) in patients under the age of 2 years old. The WAC for a one-time intravenous infusion of Zolgensma is $2.125 million per treated patient.7
Zynteglo®(betibeglogene autotemcel): The FDA has approved Bluebird bio’s Zynteglo also known as beti-cel as a one-time gene therapy to treat the underlying genetic cause of beta‑thalassemia in adult and pediatric patients who require regular red blood cell (RBC) transfusions. Beta-thalassemia, a type of inherited blood disorder, reduces the levels of normal hemoglobin and red blood cells via mutations in the beta-globin subunit; this can ultimately cause the delivery of oxygen throughout the body to be at insufficient levels. The subsequently low levels of red blood cells can result in a number of health problems, such as dizziness, weakness, fatigue, bone abnormalities, and other more serious complications. Zynteglo established the efficacy based on the achievement of transfusion independence, which is the point at which the patient maintains a pre-determined level of hemoglobin without needing any red blood cell transfusions for at least 12 months. Across two clinical studies evaluating adults and kids with transfusion-dependent beta thalassemia, 89% of the 41 patients on Zynteglo achieved transfusion independence.8 Bluebird bio anticipates its launch in 2023 with a one-time price of $2.8 million per patient.8 The list price doesn’t include the cost of hospitalization required for patients receiving the therapy.
Skysona® (elivaldogene autotemcel): The FDA approved bluebird bio’s Skysona (elivaldogene autotemcel) to slow the progression of neurologic dysfunction in boys 4-17 years of age with early, active cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy (CALD). Skysona is a one-time gene therapy that adds functional copies of the ABCD1 gene into a patient’s own hematopoietic stem cells. The accelerated approval was based on the 24-month Major Functional Disabilities (MFDs) in Phase 2/3 study ALD-102 and Phase 3 ALD-104. Patients treated with Skysona had a 72% likelihood of MFD-free survival at 24 compared to untreated patients who had only a 43% likeliood of MFD-free survival.10 Another treatment option allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (allo-HSCT). Skysona is distributed through a limited number of Qualified Treatment Centers in the US at a one-time wholesale acquisition cost of $3 million.
Hemgenix® (etranacogene dezaparvovec-drlb): The FDA has approved CSL Behring’s Hemgenix for the treatment of adults with hemophilia B who currently use factor IX prophylaxis therapy, or have current or historical life-threatening hemorrhage or have repeated, serious spontaneous bleeding episodes. Hemgenix is a one-time gene therapy product given as a single dose by IV infusion. In one study, patients who received Hemgenix had increases in factor IX activity levels, a decreased need for routine factor IX replacement prophylaxis, and a 54% reduction in annualized bleeding rate (ABR) compared to baseline.11 In a recent cost-effectiveness analysis of the drug, weighing health benefits against offset costs, the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER), an independent nonprofit research organization suggested that a fair price for the drug to be between $2.93 million and $2.96 million.12 Hemgenix has launched with a wholesale acquisition cost (WAC) of $3.5 million per one-time dose.
FDA Approved Gene Therapy – One-time administration with WAC of > $750,000
| Name | Manufacturer | Indication | WAC | Approval Date |
|
Luxturna™ (voretigene neparvovec-rzyl) |
Spark | Inherited retinal disease | $850,000 | December 2017 |
|
Zolgensma™ (onasemnogene abeparvovec-xioi) |
AveXis | Spinal muscular atrophy | $2.125 million | May 2019 |
|
Zynteglo™ (betibeglogene autotemcel) |
bluebird bio |
Transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia |
$2.8 million | August 2022 |
|
Skysona™ (elivaldogene autotemcel) |
bluebird bio | Cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy | $3 million | September 2022 |
|
Hemgenix™ (etranacogene dezaparvovec-drlb) |
CSL Behring | Hemophilia B/IV | $3.5 million | November 2022 |
The number of gene therapies for rare conditions are growing. So are the costs. An estimated 60 gene therapies will come to market in the next 10 years. Prime offers financial protection for health plans that helps preserve patient access to innovative gene therapies.
PreserveRxSM will help support Blue Plans
Prime, together with BCS Insurance Company, has announced a robust gene therapy reinsurance product called PreserveRxSM. PreserveRx seeks to protect health plans from sudden, one-time costs due to covering ultra-expensive gene therapies, while still preserving access to these potentially life-changing or curative gene therapies for members. PreserveRx covers the five FDA approved gene therapies. For self-insured employers, BCS Insurance Company offers Gene Therapy excess of loss stop loss coverage for the five FDA approved gene therapies.
Prime keeps clients ahead of the drug pipeline
Prime posts new drug approvals in its monthly pipeline updates. Prime also posts pipeline projections quarterly, in its March, June, September and December gene and cell therapy updates
Extended Gene Therapy 2023-2024 Pipeline
| Generic Name | Brand Name | Manufacturer | Indication(s) | Route of Administration | Anticipated Filing date* | Prevalence |
| valoctocogene roxaparvovec | Roctavian™ | BioMarin | Hemophilia A | IV | PDUFA: 3/31/2023 | 1,700 |
| SRP-9001 (delandistrogene moxeparvovec) | N/A |
Sarepta Therapeutics/ Roche |
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) | IV | PDUFA: 5/29/2023 | 9,000-12,000 |
| exagamglogene autotemcel (CTX-001) | N/A | Vertex | Beta-thalassemia and sickle cell disease | IV | 3Q2023 |
1,500 and 20,000 |
| lovotibeglogene autotemcel (lovo-cel) | N/A | Bluebird Bio | Sickle cell anemia | IV | 2Q2024 | ~20,000 |
| eladocagene exuparvovec | Upstaza™ | PTC Therapeutics | Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) deficiency | Intracerebral | 3Q2023 | 300 in world |
| AGTC-501 (laruparetigene zosaparvovec) | N/A | AGTC | X-linked retinitis pigmentosa | Subretinal | 4Q2023 | 20,000 in US and Europe |
|
lenadogene nolparvovec (GS-010) |
Lumevoq™ | GenSight Biologics | Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy | Intravitreal injection | 2H2023 | 6.5/million |
| OTL-201 | N/A | Orchard | MPS IIIA | IV | 1Q2024 | ~1,000 |
| LYS-SAF-302 (olenasulfligene relduparvovec) | N/A | Lysogene | MPS IIIA | Intracerebral | 1Q2024 | ~1,000 |
|
atidarsagene autotemcel (OTL-200) |
Libmeldy™ | Orchard | Metachromatic Leukodystrophy (MLD) | IV | 4Q2023 | ~460 |
| fidanacogene elaparvovec | N/A | Roche/Pfizer | Hemophilia B | IV | 3Q2023 | 3.9-6.5/million |
| fordadistrogene movaparvovec | N/A | Pfizer | DMD | IV | 4Q2023 | 9,000-12,000 |
| RP-L201 (marnetegragene autotemcel) | N/A | Rocket | Severe leukocyte adhesion deficiency type 1 (LAD-1) | IV | 1H2023 | 25-50/year severe |
| Fanconi Anemia | 2024+ | 6.25/million | ||||
|
UX111 (rebisuligene etiparvovec) |
N/A | Ultragenyx | MPS IIIA | IV | 1Q2024 | ~1,000 |
|
SB-525 (giroctocogene fitelparvovec) |
N/A |
Sangamo/ Pfizer |
Hemophilia A | IV | 3Q2024 | 1,700 |
|
FLT180a (verbrinacogene setparvovec) |
N/A | Freeline Therapeutics | Hemophilia B | IV | 2H2024 | 3.9-6.5/million |
References
- “What is Gene Therapy?” U.S. Food & Drug Administration. Accessed 4/7/20: https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/cellular-gene-therapy-products/what-gene-therapy
- net. What is the difference between ex vivo and in vivo? Accessed at: https://www.genemedi.net/i/ex-vivo-in-vivo-in-vitro
- FDA Statement from Commissioner of Food and Drug Administration Scott Gottlieb M.D. on Jan. 19, 2019. Accessed 4/7/20 at: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/statement-fda-commissioner-scott-gottlieb-md-and-peter-marks-md-phd-director-center-biologics
- MedlinePlus [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US); Gene therapy and other medical advances. Accessed at https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/understanding/therapy/procedures/
- Alliance for Regenerative Medicine; Regenerative Medicine: The Pipeline Momentum Builds – Alliance for Regenerative Medicine (alliancerm.org). https://alliancerm.org/sector-report/h1-2022-report/
- Cell and Gene Therapies Face Manufacturing Challenges, Jan 01, 2017. By Cynthia A. Challener. BioPharm International. Volume 30, Issue 1, pg 20–25. Accessed 4/7/20 at: http://www.biopharminternational.com/cell-and-gene-therapies-face-manufacturing-challenges
- https://sparktx.com/press_releases/fda-approves-spark-therapeutics-luxturna-voretigene-neparvovec-rzyl-a-one-time-gene-therapy-for-patients-with-confirmed-biallelic-rpe65-mutation-associated-retinal-dystrophy/
- https://www.novartis.com/news/media-releases/avexis-receives-fda-approval-zolgensma-first-and-only-gene-therapy-pediatric-patients-spinal-muscular-atrophy-sma
- https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-cell-based-gene-therapy-treat-adult-and-pediatric-patients-beta-thalassemia-who
- https://www.biopharmadive.com/news/bluebird-bio-gene-therapy-price-zynteglo-million/629967/#:~:text=Bluebird%20bio’s%20new%20gene%20therapy,and%20among%20the%20highest%20globally.
- https://investor.bluebirdbio.com/news-releases/news-release-details/bluebird-bio-receives-ec-approval-skysonatm-elivaldogene
- https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-gene-therapy-treat-adults-hemophilia-b
- https://icer.org/news-insights/press-releases/icer-publishes-evidence-report-on-gene-therapies-for-hemophilia-a-and-b/
Related news
Perspectives
July 25, 2024
Quarterly Drug Pipeline: July 2024
Clinical insights and competitive intelligence on anticipated drugs in development
Perspectives
July 22, 2024
Oncology Insights: 2024 ASCO Annual Meeting key findings
Findings from this year’s American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting will likely lead to clinical practice changes and U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) drug approvals or expansions
Perspectives
July 16, 2024
LISTEN NOW: Beyond the business – Stories of corporate kindness | Pharmacy Friends Podcast
In this episode, we talk about how our employees' help goes beyond our work in health care, aiding in philanthropic efforts